Kraken

- Buy, sell and trade 456 cryptos.
- Instant funding & advanced trading options.
- Join 9M+ users around the world.
Short selling is an advanced trading strategy popular across all financial markets, including cryptocurrencies. While it can be a way to profit from a downtrending market, it's not suitable for everyone.
You should have a strong grasp of trading and investing and an understanding of order types, candlestick charts, collateral and margin requirements before you get started.
This is not an endorsement of cryptocurrency or any specific provider, service or offering. It is not a recommendation to trade or use any services.
To short-sell Bitcoin, you'll need a trading account and a clearly mapped-out trading strategy.
💡 Trading tip: Many crypto exchanges offer demo or simulation trading accounts where you can practise short selling without risking any collateral.
Short selling is a popular trading strategy that involves selling an asset at a high price, ideally at the top of a range or resistance zone, and rebuying or closing the position as the price falls back to support, mean value or a downtrend.
Short sellers often use leverage to amplify position sizes. While this is common across crypto futures markets, leveraged trading is considered high risk and not recommended for beginners.
Many traders use technical analysis, charting patterns and indicators to assist this process and help understand when the market is overextended and due for a correction or likely to be rejected by a resistance zone and met by strong selling pressure.
Shorting Bitcoin can be done through a variety of different methods, including the following:
Short selling can help you to capitalise on bearish trends, pullbacks and trade mean-reversion set-ups.
It can be done on any time frame from the 1-minute chart to the weekly and is suitable for a range of trading styles, including scalping and swing trading.
Traders looking to sell Bitcoin and rebuy for a profit can do so on any centralised or decentralised exchange that supports BTC margin or leveraged trading.
Futures trading and shorting on leverage are not allowed in some jurisdictions due to regulatory restrictions.
If you plan on shorting BTC, trading on platform that is registered with AUSTRAC or ASIC is recommended. These exchanges often have better security measures in place and even insurance policies in the event of a hack or stolen funds.
Shorting any market and trading on leverage can be complicated and is considered high risk. Before shorting Bitcoin, familiarise yourself with the following concepts and tools to help better understand what's happening behind the scenes of your trade.
Leveraged short trade example:
You open a short position on BTC/USDT. You use $1,000 USDT as collateral and leverage it 10x, short selling $10,000 worth of BTC.
If BTC falls 10% and your profit target is hit, you stand to make approximately $1,000.
(10% of your initial investment * 10x leverage minus any exchange/borrowing fees).
However, if the price of Bitcoin rises by about 9% and your maintenance margin threshold is exceeded, your position will be liquidated incrementally, potentially leaving you with nothing.
To avoid liquidation, always remember to use a stop loss. Stop losses for short trades are often placed above the previous swing high. Swing highs will differ drastically based on your trading time frame and current market volatility. Calculate stop losses prior to entering the trade by using a PnL calculator or a percentage price measurement tool.
Short set-up chart example:
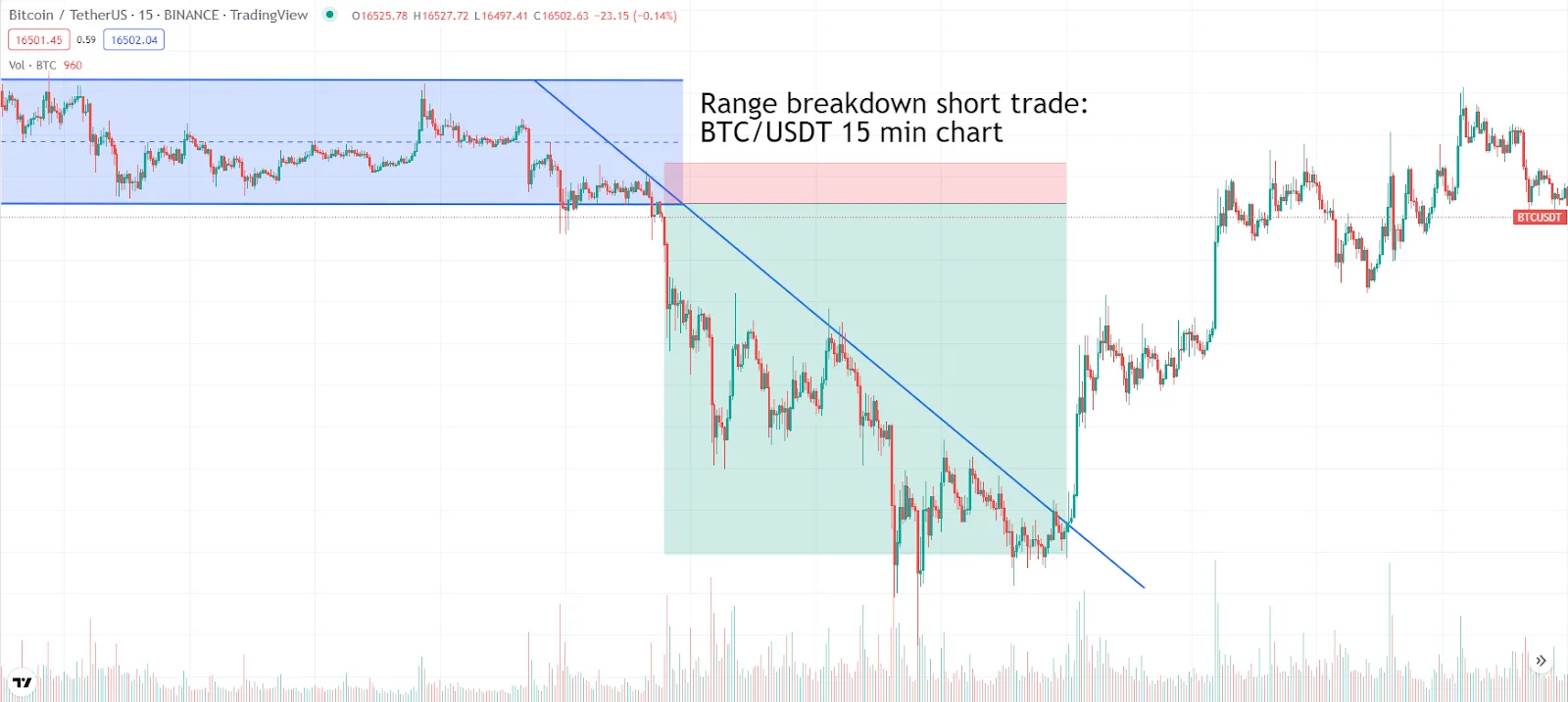
Bitcoin breaks down from a trading range on the 15-minute chart. Enter position with a stop loss placed above the range low. Depending on your trading strategy, you could take profits at numerous targets, including a test of the next support zone, the tag of a moving average or the break above the downtrend line and the signal of a momentum shift.
You can short Bitcoin in many different ways depending on your risk profile and preferred trading strategy. We've covered some of the most popular options below:
Futures contracts are a form of derivatives that allow traders to speculate on an underlying asset's price movement without holding the asset itself. They are often traded using leverage, meaning profits and losses are amplified.
There are 2 main types of future contracts. While they are similar, there are key differences that should be noted and understood.
Quarterly futures contracts have a fixed expiration date of 3 months. If this date is reached and you're still holding size on your trade, your position will be forcibly closed by the exchange regardless of whether it is in profit or loss.
Perpetual futures contracts, or "perps" are the most popular way to short Bitcoin, with billions of dollars' worth of futures contracts bought and sold daily. Perps are traded the same way as regular futures, with the main difference being that the contracts do not have an expiration date and can be held indefinitely.
Futures and leveraged trading are recommended for advanced users. Mismanaged trades have the potential to unravel quickly and your collateral can be liquidated (taken by the exchange to cover losses).
We currently don't have that product, but here are others to consider:
How we picked theseWe currently don't have that product, but here are others to consider:
How we picked theseGetting started with spot margin trading is simple and can be used to amplify your profits using leverage. Keep in mind that this works both ways, and losses will depend on how you manage your risk and stop loss.
Once you have opened and funded a margin account, you can borrow collateral and start trading. Most exchanges offer 3–10x leverage. You will see some exchanges that offer more than that, but these should be reserved for experts only, as every additional point of leverage increases your risk.
Assume you have a $10,000 account size and leverage it 3x – you now have $30,000 to use for your trades.
If you sell 1 BTC for $30,000 and the price decreases to $27,000, you stand to make about $3,000 profit, as opposed to $1,000 if you had not leveraged your account.
Inversely, if the price of Bitcoin rises and you do not have a stop loss in place, your entire trading account could be forcibly closed and your collateral liquidated.
Borrowing fees, trading fees and slippage should also be considered when trading spot margin.
Bitcoin CFDs or contracts for difference are similar to futures trades in that your PnL is calculated based on the difference in price between the time you open and close your position.
The key difference is that CFDs are settled in fiat currency, not digital stablecoins or cryptocurrencies such as USDT or Bitcoin.
CFDs are traded through traditional financial brokers rather than on centralised or decentralised cryptocurrency exchanges. They are considered high-risk investment vehicles and should only be used by experienced traders.
A popular CFD trading strategy is what's known as hedging – holding both long and short positions simultaneously. If you're holding an open futures long position, you could short Bitcoin CFDs hedging your trade and mitigating risk. If the trade is managed correctly, one position will remain in profit regardless of market conditions.
However, hedging is a complicated strategy and not recommended for beginners as it typically does not involve a stop loss. Calculating risk can also be complicated.
Options are derivatives contracts that come in 2 forms: calls and puts. Put options allow you to short Bitcoin by speculating that the price will drop, similar to a futures trade.
However, unlike futures, losses are limited to the purchase price of the options contract and cannot rise or fall indefinitely.
To short Bitcoin, you would purchase a put option that would give you the option, but not the obligation to sell Bitcoin at today's price at a later date. The purchase price is referred to as the strike price.
Options are often used to hedge positions – trade both long and short positions simultaneously to help mitigate risk.
Options can be complicated and are recommended for advanced traders or those with a background in traditional financial instruments.
Leveraged tokens are derivatives that traders can hold on crypto spot markets rather than futures-only exchanges.
Leveraged tokens represent a basket of perpetual contracts and move based on futures price fluctuations.
Unlike futures or margin trading, leveraged tokens allow you to short Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies without the risk of liquidation or the need to monitor a maintenance margin.
By purchasing a BTCDOWN leveraged token, you can short sell with a targeted leverage range between 1.25x and 4x, helping to maximise profitability on downtrends and minimise losses during uptrends.
If the price of BTC falls, BTCDOWN will add leverage in an attempt to increase profits. Inversely, if BTC rises in price, your leveraged token will auto-rebalance, reducing the margin to cap losses and avoid liquidation.
Short selling Bitcoin requires holding BTC on the spot market instead of using collateral such as USDT for leveraged trading.
As it is not a derivative market, it does not allow for leverage and is the lowest risk, lowest reward strategy. Spot traders can sell and rebuy Bitcoin for substantial gains if done correctly.
Spot market short-sellers are typically those who are holding Bitcoin long term. They will ride the trend up, sell near the top and rebuy for a gain or accumulate additional BTC as the market corrects. This may also be referred to as swing trading.
Although liquidation is not a concern, if the market moves against you, you may be forced to purchase BTC at a higher price than you sold it for.
We currently don't have that product, but here are others to consider:
How we picked theseTaking a short position and the associated cost will depend on the exchange you choose to use and its fee structure.
Typically, taker fees are higher than maker fees as you're removing liquidity from the market instead of providing additional tradable funds.
Another consideration when trading on leverage is liquidation fees. This is the percentage the exchange charges as a penalty for exceeding your margin ratio. Liquidation penalties vary depending on exchanges. They are typically high, often 5% or more.
Market volatility and risk management are the most important factors when taking any trade. Only open a position with an exit strategy or stop loss set at an amount you're willing to risk.
There is no ''perfect set-up'' for short selling, but there are some things to consider when planning your trades.
Investing and shorting Bitcoin are different styles of trading.
Investors hold long positions, generally on spot markets or low-leverage position trades. Investors often trade without stop losses as the chance of liquidation for a low-leverage position is decreased. Spot market trades can fall drastically, but without leverage, there is no chance of liquidation.
Bitcoin short traders open positions, typically on leverage, expecting the price of BTC to fall or trend down. If the trade plays out favourably, the position is closed and a profit is realised. If the position runs offside, a stop loss should be placed and triggered to avoid substantial losses.
Trading Bitcoin comes with high risk, especially when leverage is added to a position. Things to consider before short selling Bitcoin include:
Trading and investing of any kind have associated risks. Digital assets are considered especially risky as they are often more volatile than traditional assets, including high market cap stocks, FX and precious metals such as gold.
The risks of trading cryptocurrencies are amplified when using leverage. If trades are mismanaged, losses can quickly accumulate. Before short selling Bitcoin, it is important to have a firm grasp of trading spot markets, investing, volatility, margin and risk management.
Many exchanges offer demo trading accounts to help you understand the fundamentals before trading using your capital.
Disclaimer: Cryptocurrencies are speculative, complex and involve significant risks – they are highly volatile and sensitive to secondary activity. Performance is unpredictable and past performance is no guarantee of future performance. Consider your own circumstances, and obtain your own advice, before relying on this information. You should also verify the nature of any product or service (including its legal status and relevant regulatory requirements) and consult the relevant Regulators' websites before making any decision. Finder, or the author, may have holdings in the cryptocurrencies discussed.
We reviewed more than 20 crypto exchanges to find you the ones best suited to day trading cryptocurrency.
Day trading crypto involves making short-term trades to take advantage of small price fluctuations.
You can trade crypto futures in Australia, but your options may be limited.
Compare a list of gold-backed cryptocurrencies.
Your detailed guide to cryptocurrency trading bots, how they work and the benefits and risks you need to consider when choosing a crypto trading bot.
There’s much to gain and lose in the volatile cryptocurrency market. If you want to make the best decisions, then you need to understand how to do a technical analysis. This guide from finder will tell you everything you need to know.
Learn about OTC cryptocurrency trading, what it is and how it works in this comprehensive guide.
Learn how crypto arb trading works and how to get started with this guide.
Find out what exactly bitcoin futures trading is, where to get started and how to pick the right trading site.